Architectural Set Drawings
January 17, 2024
The Power of Your Corporate Profile
April 26, 2024| Uncover the fascinating world of drone mapping, also known as drone surveying or aerial surveying, in this comprehensive article. |
Drone Mapping (also known as Drone Surveying or Aerial Surveying)
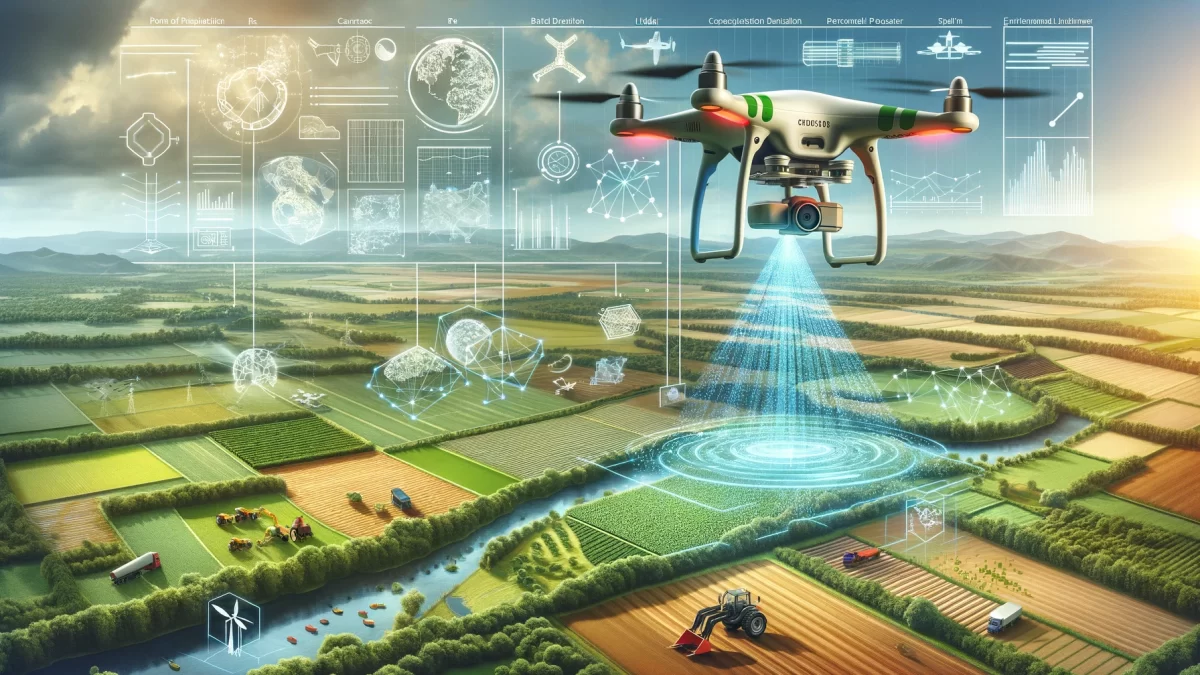
Drone mapping, also referred to as drone surveying or aerial surveying, is a rapidly evolving technology that has revolutionized various sectors, including agriculture, construction, environmental conservation, and urban planning. This technique involves the use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, equipped with high-resolution cameras or sensors to capture aerial data. This data is then processed using specialized software to generate detailed and accurate maps or 3D models of the surveyed area.
Drone mapping offers numerous advantages over traditional surveying methods. It provides a safer, faster, and more cost-effective way of collecting high-quality data. Moreover, it allows for the capture of data in inaccessible or hazardous areas, thus expanding the scope of mapping and surveying. This article delves into the intricacies of drone mapping, exploring its various applications, offering valuable insights, and highlighting the innovative edge of this transformative technology.
Understanding Drone Mapping: A Comprehensive Overview
Drone mapping is a complex process that involves several steps, from flight planning and data collection to data processing and map creation. The quality of the final map or model depends on various factors, including the type of drone and sensor used, the flight altitude and speed, the overlap of the images, and the accuracy of the ground control points.
One of the key components of drone mapping is the drone itself. Drones used for mapping are typically equipped with GPS and inertial measurement units (IMUs) to maintain stable flight and accurate positioning. They also carry high-resolution cameras or other sensors to capture aerial data. Some drones are also equipped with Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) sensors, which use laser pulses to measure distances and generate highly accurate 3D models.
Flight Planning and Data Collection
Flight planning is a crucial step in drone mapping. It involves defining the area to be mapped, setting the flight altitude and speed, and determining the image overlap. The flight plan is typically programmed into the drone’s autopilot system, which controls the drone’s flight path and triggers the camera or sensor at the right intervals to capture the required data.
Data collection is carried out by the drone’s camera or sensor. The most common method of data collection is photogrammetry, which involves taking overlapping photos of the ground from different angles. These photos are then stitched together to create a map or 3D model. Other methods of data collection include LiDAR and multispectral imaging, which capture different types of data and are used for specific applications.
Data Processing and Map Creation
Once the data is collected, it is processed using specialized software. The software aligns the images, corrects for distortions, and stitches the images together to create a seamless map or 3D model. This process, known as photogrammetric processing, involves complex algorithms and can take several hours or even days, depending on the amount of data and the processing power of the computer.
The final output of drone mapping is a georeferenced map or 3D model that can be viewed and analyzed using GIS software. The map or model can be overlaid with other data layers, such as property boundaries or infrastructure networks, to provide a comprehensive view of the surveyed area. This allows for detailed analysis and decision-making, making drone mapping a valuable tool in various fields.
Applications of Drone Mapping
Drone mapping has a wide range of applications across various sectors. In agriculture, for example, drone maps can be used to monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and manage pests and diseases. In construction, drone maps can be used to monitor progress, manage resources, and ensure safety. In environmental conservation, drone maps can be used to monitor wildlife, assess habitat conditions, and track changes over time.
One of the most promising applications of drone mapping is in disaster management. Drone maps can provide real-time information about disaster-stricken areas, helping emergency responders to assess the situation, plan their response, and monitor recovery efforts. Drone maps can also be used in urban planning, infrastructure management, and land surveying, among other fields.
Agriculture
In agriculture, drone mapping is used for precision farming, a practice that involves the use of technology to optimize crop production. Drone maps can provide detailed information about the condition of the crops, the soil, and the environment, allowing farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. This can lead to increased crop yields, reduced environmental impact, and improved profitability.
Drone mapping can also be used for crop scouting, a practice that involves inspecting crops for signs of pests, diseases, or other problems. By providing a bird’s-eye view of the field, drone maps can help farmers to identify problem areas and take corrective action before the problem spreads. This can save time and resources, and prevent crop losses.
Construction
In construction, drone mapping is used for site planning, progress monitoring, and quality control. Drone maps can provide a detailed and up-to-date view of the construction site, allowing project managers to plan activities, allocate resources, and monitor progress. This can lead to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and better project outcomes.
Drone mapping can also be used for safety inspections, a practice that involves checking the construction site for potential hazards. By providing a high-resolution view of the site, drone maps can help safety officers to identify hazards, assess risks, and take preventive measures. This can reduce accidents, improve worker safety, and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Insights from Drone Mapping
Drone mapping provides valuable insights that can inform decision-making in various fields. These insights can be derived from the analysis of drone maps and the integration of drone data with other data sources. For example, in agriculture, drone maps can reveal patterns of crop health, soil moisture, and nutrient levels, helping farmers to optimize their farming practices. In construction, drone maps can reveal patterns of progress, resource usage, and safety risks, helping project managers to improve their project management practices.
One of the key insights from drone mapping is the ability to monitor changes over time. By comparing drone maps from different time periods, it is possible to track changes in the landscape, the environment, or the infrastructure. This can provide valuable information for land management, environmental conservation, urban planning, and other fields.
Monitoring Changes Over Time
Monitoring changes over time is one of the most powerful applications of drone mapping. This involves taking drone maps at regular intervals and comparing them to track changes. This can be used to monitor the progress of a construction project, the growth of a crop, the spread of a disease, or the impact of a natural disaster.
Change detection can be done manually, by visually comparing the maps, or automatically, by using software that can detect changes based on color, texture, or other features. This can provide timely and accurate information, allowing for quick response and effective management.
Integrating Drone Data with Other Data Sources
Another valuable insight from drone mapping is the ability to integrate drone data with other data sources. This involves overlaying drone maps with other data layers, such as satellite images, ground surveys, or GIS data. This can provide a more comprehensive view of the area, allowing for more detailed analysis and better decision-making.
Integration of drone data can be done using GIS software, which can handle multiple data layers and perform complex spatial analyses. This can be used to assess the suitability of a site for construction, the productivity of a farm, the vulnerability of a community to disasters, or the health of an ecosystem, among other applications.
Innovations in Drone Mapping
Drone mapping is a rapidly evolving field, with new innovations constantly emerging. These innovations are driven by advancements in drone technology, sensor technology, and data processing technology. They are also driven by the growing demand for drone mapping services in various sectors.
One of the key innovations in drone mapping is the development of more advanced drones. These drones are equipped with better cameras, more accurate GPS systems, and more powerful processors. They are also equipped with more advanced flight control systems, which allow for more precise and stable flight. This leads to higher quality data and more accurate maps.
Advancements in Drone Technology
Advancements in drone technology have led to the development of more capable and reliable drones. These drones are equipped with better cameras, more accurate GPS systems, and more powerful processors. They are also equipped with more advanced flight control systems, which allow for more precise and stable flight.
One of the key advancements in drone technology is the development of autonomous drones. These drones can fly pre-programmed routes without human intervention, allowing for more efficient data collection. They can also react to changes in the environment, such as wind gusts or obstacles, ensuring safe and stable flight.
Advancements in Sensor Technology
Advancements in sensor technology have led to the development of more advanced sensors for drone mapping. These sensors can capture more detailed and accurate data, leading to higher quality maps. They can also capture different types of data, such as thermal data or multispectral data, expanding the applications of drone mapping.
One of the key advancements in sensor technology is the development of LiDAR sensors for drones. These sensors use laser pulses to measure distances, allowing for the creation of highly accurate 3D models. They can also penetrate vegetation and other obstacles, allowing for the mapping of hidden features.
Advancements in Data Processing Technology
Advancements in data processing technology have led to the development of more advanced software for drone mapping. This software can process large amounts of data more quickly and accurately, leading to faster map creation. It can also perform more complex analyses, such as change detection or 3D modeling, expanding the insights from drone mapping.
One of the key advancements in data processing technology is the development of cloud-based software for drone mapping. This software allows for the processing of drone data on powerful cloud servers, reducing the need for high-end computers. It also allows for the sharing and collaboration of drone maps, enhancing the utility of drone mapping.
Conclusion
Drone mapping, also known as drone surveying or aerial surveying, is a transformative technology that has revolutionized various sectors. It provides a safer, faster, and more cost-effective way of collecting high-quality data, expanding the scope of mapping and surveying. With advancements in drone technology, sensor technology, and data processing technology, drone mapping is set to become even more powerful and versatile in the future.
From agriculture and construction to environmental conservation and disaster management, drone mapping offers numerous applications and valuable insights. It allows for detailed analysis and decision-making, making it a valuable tool in various fields. As drone mapping continues to evolve, it is expected to bring even more innovations and opportunities, shaping the future of mapping and surveying.



